🌡️ محتوى الرطوبة Moisture Content مقابل النشاط المائي Water Activity
مرسل: الجمعة نوفمبر 21, 2025 6:15 pm
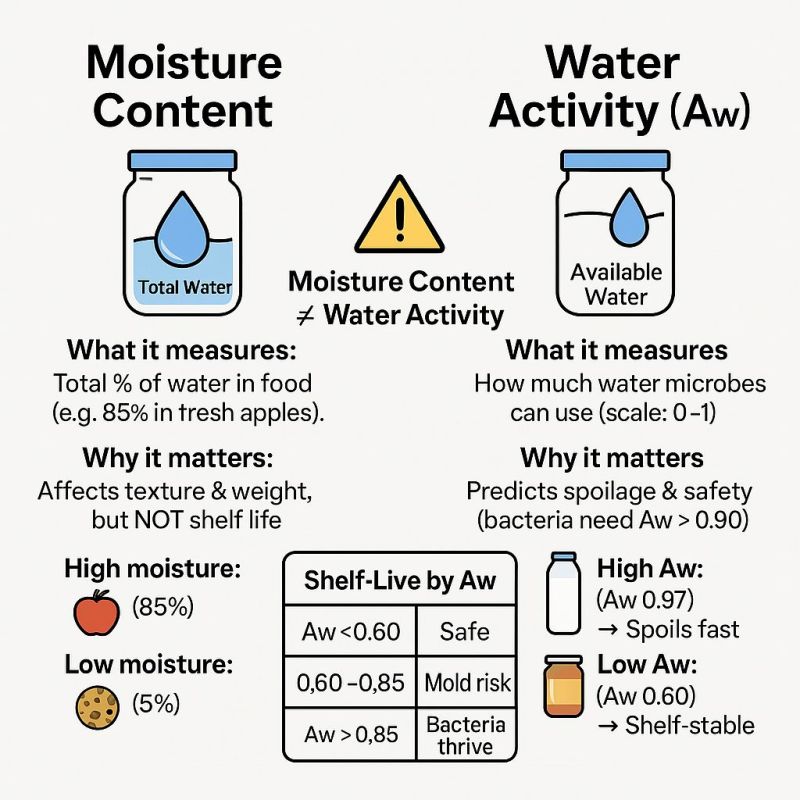
🌡️ Moisture Content vs Water Activity:
In food processing and quality management, moisture content and water activity (aw) are two of the most important measurements—but they are often misunderstood. Knowing the difference is essential for controlling shelf life, texture, and microbial safety.
🔹 Moisture Content: Total Water in the Product. Moisture content tells you how much water is present, expressed as a percentage.
It influences:
-Product texture (crisp vs soft)
-Weight declaration and yield
-Drying efficiency
-Cost and formulation control
*But moisture content does not determine microbial stability.
🔹 Water Activity (aw): free available water in food, defined as the ratio of a food's vapor pressure to the vapor pressure of pure water. Water activity measures available water, not total water (Water That Microbes Can Use)
This is what microbes need to grow—and what drives chemical reactions like browning, oxidation, and enzymatic activity.
Typical microbial growth limits:
Bacteria: aw > 0.90
Yeast: aw > 0.80
Mould: aw > 0.60
Because of this, water activity is a true predictor of shelf life and spoilage risk.
🔹 Why Two Foods With the Same Moisture Act Differently
Ingredients such as salts, sugars, and proteins can bind water, lowering aw even when moisture content is high.
Example:
Jam has high moisture content but low aw due to high sugar—so it doesn't spoil quickly.
A soft cookie may have low moisture but high aw—making it more spoilage-prone.
This difference is crucial for product developers and QA teams.
🔹 Why Water Activity Is a CCP in Many Standards
Systems like BRCGS, HACCP, and FSMA emphasize aw control because it directly affects:
-Microbial safety
-Chemical stability
-Preservative requirements
-Overall product shelf life
-Water activity is often more reliable than moisture content for hazard control.
🔹 Key Takeaway
Moisture content tells us how much water is present.
Water activity tells us how water behaves—and whether the product is safe.
https://www.linkedin.com/mwlite/feed/posts/zeeshanft_moisture-content-vs-water-activity-activity-7396781691303899136-P98q?utm_source=share&utm_medium=member_android&rcm=ACoAABG_IYwBEFoQoeYtJNIF1NzAvC8HDe-lKJ4#:~:text=%F0%9F%8C%A1%EF%B8%8F%20Moisture%20Content%20vs,product%20is%20safe.
🌡️ محتوى الرطوبة Moisture Content مقابل النشاط المائي Water Activity :
في مجال تصنيع الأغذية وإدارة الجودة، يُعد كل من محتوى الرطوبة و النشاط المائي (aw) من أهم القياسات — ولكن غالبًا ما يحدث سوء فهم بينهما. معرفة الفرق بينهما أمر أساسي للتحكم في مدة الصلاحية، القوام، والسلامة الميكروبية.
---
🔹 محتوى الرطوبة: إجمالي المياه في المنتج
محتوى الرطوبة يخبرك بكمية الماء الموجودة في المنتج كنسبة مئوية.
ويؤثر على:
قوام المنتج (مقرمش/طري)
الوزن المُعلن والعائد الإنتاجي
كفاءة التجفيف
التحكم في التكلفة والتركيبة لكن محتوى الرطوبة لا يحدد الاستقرار الميكروبي.
---
🔹 النشاط المائي (aw): الماء الحر المتاح في الغذاء
هو نسبة ضغط بخار الغذاء إلى ضغط بخار الماء النقي.
النشاط المائي يقيس كمية الماء المتاح للاستخدام، وليس كمية الماء الكلية (أي الماء الذي يمكن للكائنات الدقيقة استخدامه).
وهذا هو ما تحتاجه الميكروبات للنمو—وهو أيضًا ما يقود التفاعلات الكيميائية مثل الاسمرار، الأكسدة، والنشاط الإنزيمي.
حدود نمو الميكروبات :
البكتيريا: aw > 0.90
الخمائر: aw > 0.80
العفن: aw > 0.60
ولهذا، يعتبر النشاط المائي مؤشرًا حقيقيًا لمدة الصلاحية وخطر التلف.
---
🔹 لماذا يتصرف غذاءان لهما نفس محتوى الرطوبة بشكل مختلف؟
بعض المكونات مثل الأملاح، السكريات، والبروتينات يمكن أن تربط الماء، مما يخفض النشاط المائي حتى لو كان محتوى الرطوبة مرتفعًا.
مثال:
المربى يحتوي على رطوبة عالية ولكن aw منخفض بسبب السكريات المرتفعة—لذلك لا يفسد سريعًا.
كوكيز طري قد يحتوي على رطوبة منخفضة ولكن aw مرتفع—مما يجعله أكثر عرضة للتلف.
هذا الاختلاف مهم جدًا لمطوري المنتجات وفِرَق الجودة.
---
🔹 لماذا يُعد النشاط المائي نقطة تحكم حرجة (CCP) في العديد من المعايير؟
الأنظمة مثل BRCGS، HACCP، وFSMA تركز على التحكم في aw لأنه يؤثر مباشرة على:
السلامة الميكروبية
الاستقرار الكيميائي
الحاجة للمواد الحافظة
مدة صلاحية المنتج
كما أن النشاط المائي غالبًا ما يكون أكثر موثوقية من محتوى الرطوبة في التحكم بالمخاطر.
---
محتوى الرطوبة يخبرنا بكمية الماء الموجودة.
النشاط المائي يخبرنا بكيفية تصرف هذا الماء—وما إذا كان المنتج آمنًا أم لا.